Fast and simple loan to make rental bonds and moving expenses simple.
-
-
-
Resources
-
Company
The two main types of interest rates you can get on a personal or car loan are fixed and variable interest rates. Both options have their pros and cons, and it’s essential to understand these before committing to one, as they can both suit different types of borrowers depending on their needs.
This guide aims to inform you about the pros and cons of fixed and variable rates so you can choose the one that best suits you.
This article was originally written by Jemima Kelly, November 2022.
On this page:
A fixed-rate loan guarantees a fixed interest rate for a set period of time, known as the fixed term. This period is usually for several years, which on a personal loan means they can be fixed for the entire time.
Having a fixed interest rate means that your lender can’t increase your rate no matter how much interest rates fluctuate, and you only have to pay the amount of interest that you agreed on if you meet your repayments.
This secures your repayment amounts for the loan period, which usually ranges from one to five years on personal loans. As such, a fixed-rate loan saves you from having to predict your future repayments if they were to go up.
A fixed-rate loan generally suits people who like to stick to a budget and want to make consistent repayments. At Jacaranda Finance, our loans exclusively offer fixed interest rates for loan terms of up to 36 months.
On the other hand, fixed rates might not be the better option if interest rates are falling. You could potentially miss out on some ongoing savings if lenders were to pass on a series of cash rate decreases, for example.
The cash rate is the interest rate at which banks and lenders borrow money; it’s essentially the cost of funding. If this rate is high, lenders generally need to compensate for this with an interest rate increase of their own across many of their lending products,
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) meets eight times a year to decide on the cash rate, either increasing, decreasing or holding the current rate. If an interest rate increase is determined, lenders are encouraged to move and raise their rates at the same amount.
Here’s how the cash rate target has moved over the years:
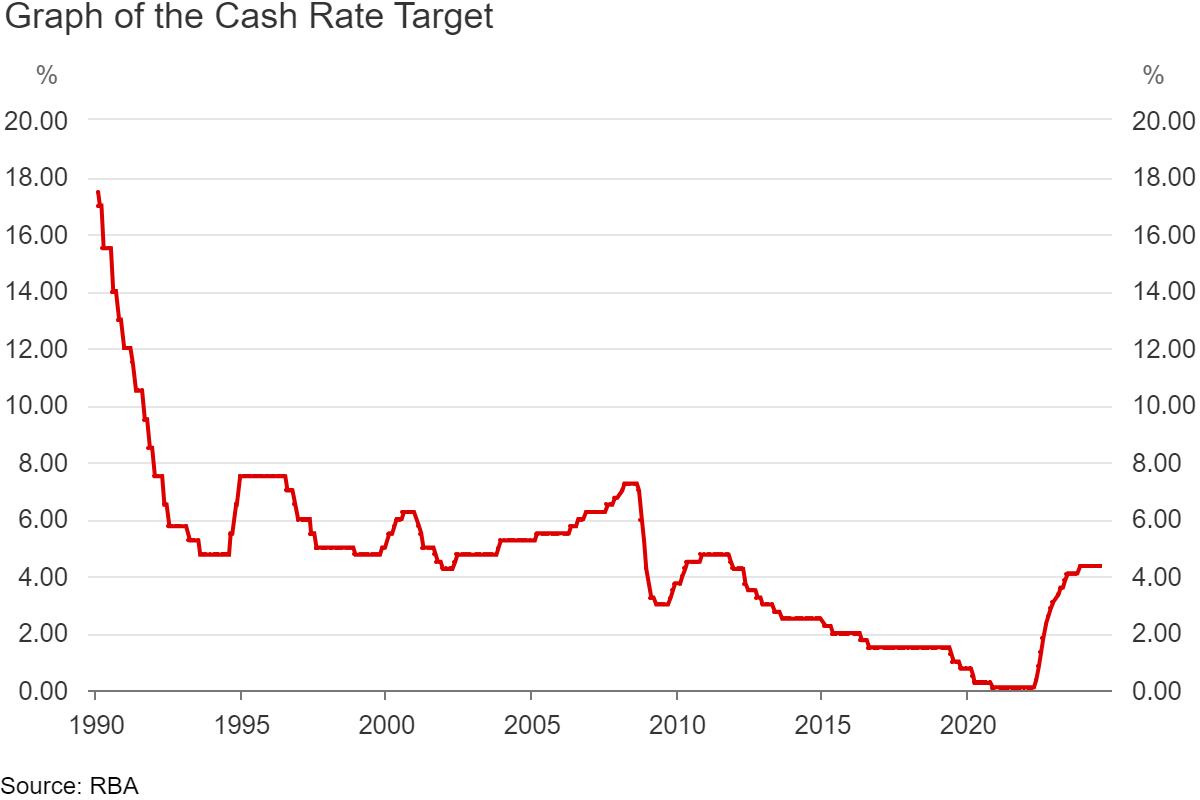
That significant spike in the last couple of years is something you’re likely familiar with. The cash rate went from a record low of 0.10% in April 2022 to 4.35% today. The RBA has raised the cash rate 13 separate times since then by over 4%!
Fixed rates have a number of advantages, which generally include:
Did you know? If you were on a variable-rate loan, your interest rate could have gone up by more than 4% p.a in just a couple of years!
Fixed-rate loans have their downsides, too, such as:
Did you know? Unlike many lenders with fixed rates, Jacaranda Finance does not charge extra repayment fees or fees for paying off your loan early. In fact, we encourage you to do so!
A variable-rate loan does not set one specific interest rate for the duration of the loan. Instead, the interest rate can change due to a number of factors, including the Reserve Bank of Australia’s official cash rate decisions, the lender’s market position, competitor movements and the economy as a whole.
As such, your interest rate could be different from month to month, although your lender must give you advance notice in writing when they intend to change your rate and the size of the increase.
A variable interest rate loan can give you access to additional features that fixed-rate loans generally don’t have. One of these main features is having no extra repayment fees or break costs, although, as we mentioned earlier, Jacaranda also doesn’t charge these.
This feature can be helpful if you plan on paying off your loan faster than the agreed-upon loan period, and it could also help you save on interest.
A variable-rate loan can be well suited to many different financial situations. For example, it can be helpful for people who are okay with taking a bit more of a risk and plan on paying off their loan in a shorter period of time. Some of the advantages include:
Variable-rate loans aren’t perfect and have flaws, which you should be aware of before deciding to apply for one. These include:
Need help budgeting?
As the graph below shows, lenders’ rates tend to follow the cash rate carefully across their entire product suite. We’ve highlighted the interest rates (from the Reserve Bank’s date) on both variable-rate home loans and newly funded personal loans for each month in the past four or so years.
For larger loans like home loans, many lenders offer split-rate loans. This type of loan lets you take advantage of both fixed and variable interest rates by splitting a portion of your loan into each.
You could, for example, choose to make 50% of your loan variable and the other 50% fixed, giving you the best of both worlds and balancing out the negatives of each.
However, split-rate loans are generally not available on personal or car loans, as these loans tend to be too small.
Both fixed-rate and variable-rate loans can be helpful depending on the circumstances: who is borrowing the money, how much they’re borrowing, the economic environment at the time, and more.
These are all critical factors that can influence which one is better. Choosing the right rate for your unique situation is very important. This ensures you aren’t paying too much in repayments and can help you reach your financial goals quicker.
If you’re confident in your finances and budgeting skills and aren’t worried about rising interest rates, you might want to consider a variable-rate loan. This is because you can have more flexibility in making your repayments and won’t be locked into the loan term by break costs.
If you’re looking for some stability, however, and need a personal loan for a particular reason, like a holiday or house renovations, a fixed-rate loan might be the more suitable option.
This is because your monthly repayments will stay the same, meaning you can budget more efficiently. It can also provide you with certainty that you can repay the loan over the loan period.
When considering which loan is right for you, there’s more to differentiate between the different products than just whether they offer fixed or variable interest rates.
Personal and car loans can also be secured, unsecured, interest-only or charge both principal and interest.
Here’s what each of those things means.
Principal and interest repayments (P&I) are the more common form of loan repayment, especially with car and personal loans. With these, you pay off both the loan principal (the amount you borrowed) and the interest (the cost of borrowing) over the loan term.
As an example, let’s say you borrow $10,000 at 15%p.a. for five years (no fees, fixed rate). The principal amount here is $10,000, while the 15% will also be charged, adding to your repayments.
With principal and interest repayments, you would pay $238 per month and $14,274 in total throughout this loan.
Interest-only (IO) repayments, on the other hand, allow you to pay just the interest on your loan for a set period of time, which can result in lower monthly payments initially.
However, after the interest-only period ends, you are required to start paying off the loan principal, often resulting in higher ongoing and overall costs.
This type of repayment might be helpful for short-term financial goals but can be riskier in the long term because the entire principal must be repaid later.
Using the above example, adding a two-year interest-only period to your $10,000 loan could make a big difference. With a two-year IO period, your monthly repayments would initially be $125 before climbing steeply to $347 when reverting to P&I repayments.
This loan would cost $15,480 in total over five years—more than $1,000 extra compared to P&I repayments from the outset.
It’s also essential to understand the distinction between secured and unsecured loans.
Secured loans require you to put up an asset (like a car or house) as security, typically allowing for more competitive rates and fees. However, if you fail to repay your loan, the lender could repossess that asset.
Unsecured loans, on the other hand, don’t require security but often come with higher interest rates because they pose a higher risk to the lender.
See the key differences between secured and unsecured loans here for more information.
When evaluating loan options, it's crucial to look at the comparison rate alongside the advertised interest rate. The comparison rate gives a clearer picture of the true cost of the loan because it includes specific fees and charges in addition to the interest rate.
Simply put, a comparison rate can help you compare loans based on a more accurate view of their cost. This can be especially helpful when looking at a loan that might advertise a low interest rate but carries some expensive ongoing or upfront fees to compensate.
In Australia, lenders are legally required to display the comparison rate alongside the advertised interest rate whenever an individual rate is displayed.
Jacaranda Finance offers Fixed-Rate Personal and Car Loans. Unlike many others, our fixed-rate loans offer flexible extra repayments at no extra cost, and you won’t be charged anything for paying off your loan early.
This can provide one of the main benefits of variable loans without compromising the security of unchanged repayments.
With loans from $3,000 up to $25,000 and loan terms as long as 36 months, our loans could be the financial solution you’ve been searching for.
Check if you qualify without impacting your credit score today: You can apply in as little as 5-12 minutes1 and could receive an outcome on your application on the same day2.